Hi! I am Shengjie Luo (罗胜杰), a final-year Ph.D. student at School of Intelligence Science and Technology in Peking University, advised by Prof.Liwei Wang and Prof.Di He. Before that, I finished my undergraduate study at ShenYuan Honors College in Beihang University, majoring in Computer Science. I have been a research intern at Microsoft Research Asia.
My main research area lies in machine learning, with special interests in providing insights into fundamental deep learning models and algorithms (Transformers, GNNs, Geometric Deep Learning), covering their expressiveness, efficiency and effectiveness. I have published several works in top-tier machine learning conferences such as ICLR, NeurIPS, ICML. I received the Outstanding Paper Award at ICLR 2023 (Top 4/4966) and won the 1st place winner prize of KDD CUP 2021.
If you are interested in collaborating with me or want to have a chat, always feel free to contact me through e-mail or WeChat :)
🔥 News
- 2025.01: One paper is accepted at ICLR 2025!
- 2024.09: Two papers are accepted at NeurIPS 2024!
- 2024.05: Two papers are accepted at ICML 2024!
- 2024.01: Our paper “Enabling Efficient Equivariant Operations in the Fourier Basis via Gaunt Tensor Products” is selected as Spotlight Presentation (top 4.96%) at ICLR 2024, see you in Vienna!
- 2024.01: One paper is accepted at ICLR 2024!
- 2023.03: Our paper “Rethinking the Expressive Power of GNNs via Graph Biconnectivity” received the
ICLR 2023 Outstanding Paper Award (top 4/4966)! - 2023.01: Two papers are accepted at ICLR 2023!
- 2022.11: Transformer-M has been used by all Top-3 winners in PCQM4Mv2 Track, 2nd OGB Large-Scale Challenge, NeurIPS 2022!
- 2022.09: One paper is accepted at NeurIPS 2022!
- 2021.09: Two papers are accepted at NeurIPS 2021!
- 2021.06: Graphormer won the 1st place in PCQM4M Track, OGB Large-Scale Challenge, KDD CUP 2021!
- 2021.05: One paper is accepted at ICML 2021!
📝 Selected Publications (Full List)
* denotes equal contribution, † denotes correspondence authorship.
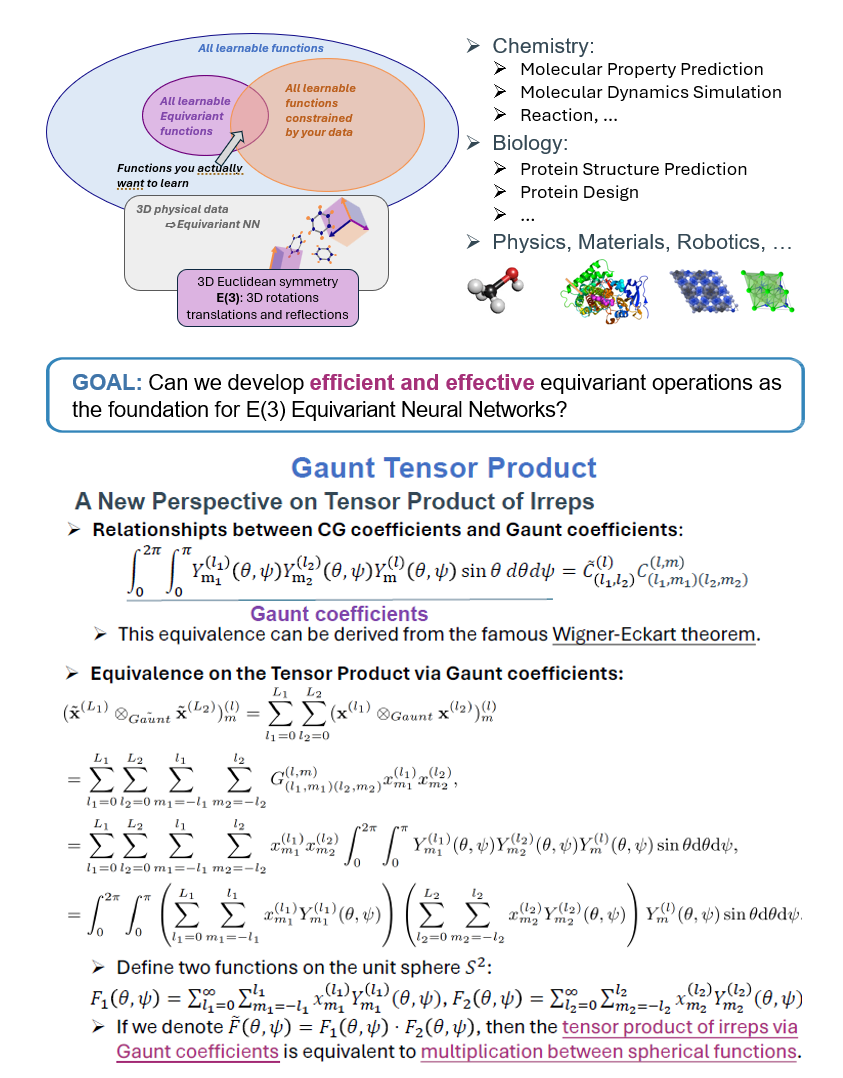
[ICLR 2024 Spotlight (top 4.96%)] Enabling Efficient Equivariant Operations in the Fourier Basis via Gaunt Tensor Products
Shengjie Luo*, Tianlang Chen*, Aditi S. Krishnapriyan
- We develop a brandly new and systematic method to substantially improve the efficiency of the mainstream E(3) equivariant operations, tensor product of irreps, opening up a new opportunity to pushing the frontier of Geometric Deep Learning and its application in Science.
- A new perspective: we reveal the relationship between Clebsch-Gordan coefficients and Gaunt coefficients spherical harmonics, connecting tensor product of Gaunt coefficients with integrals of products between three spherical functions.
- A new opportunity: instead of using spherical harmonics, products between spherical functions expressed as 2D Fourier Basis can be accelerated.
- We introduce Gaunt Tensor Product, a principled approach to accelerate Tensor Product of Irreps, the complexity of which is reduced to just O(L^3) instead of O(L^6).
- Our method opens up a new pathway for revolutionizing modern E(3) Equivariant Neural Networks, and extensive experiments further demonstrate the efficiency and generality of our Gaunt Tensor Product approach.
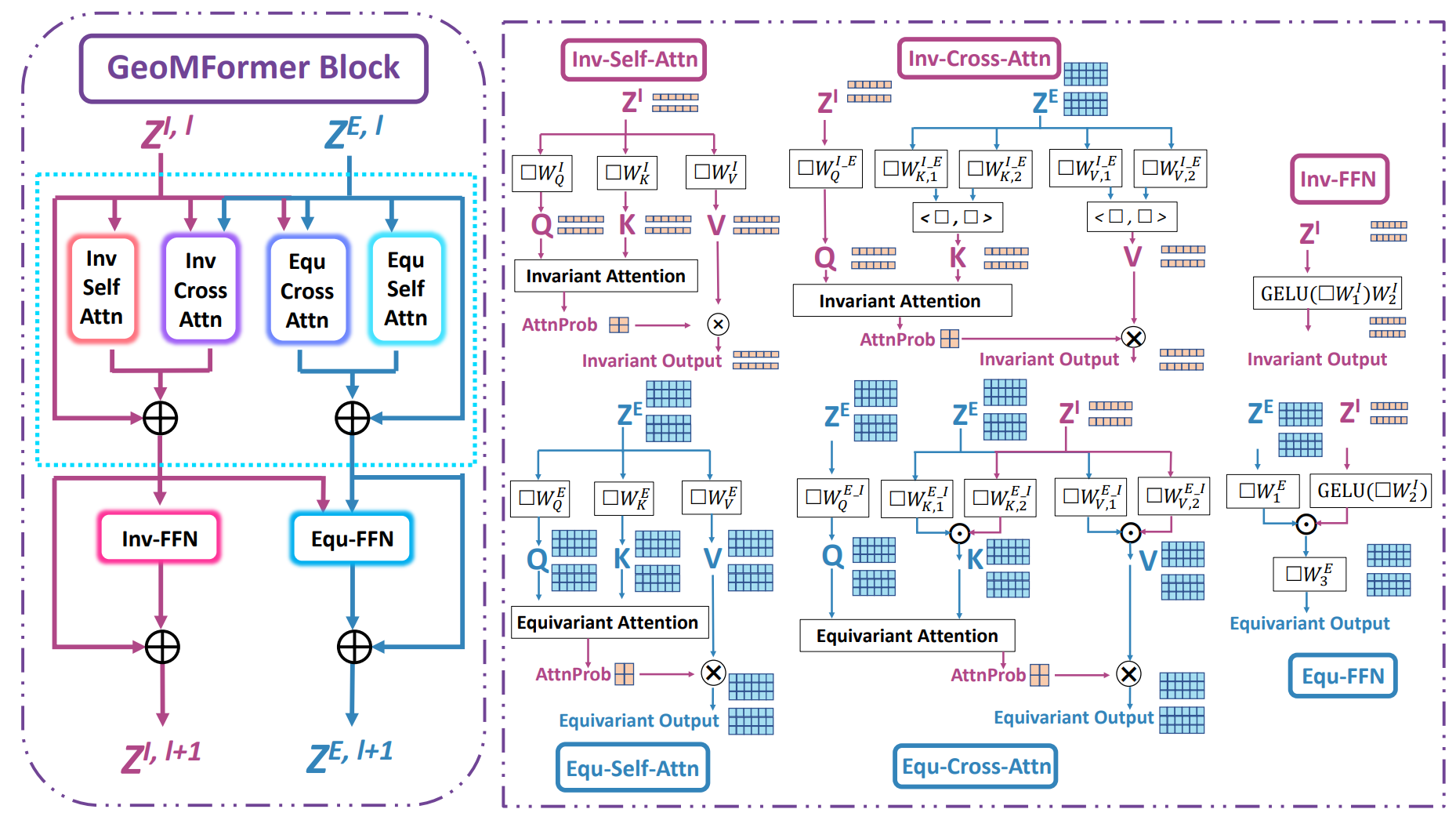
[ICML 2024] GeoMFormer: A General Architecture for Geometric Molecular Representation Learning
Tianlang Chen*, Shengjie Luo*†, Di He, Shuxin Zheng, Tie-Yan Liu, Liwei Wang
- We develop a Transformer-based Geometric Molecular model called GeoMFormer, which can effectively perform both invariant and equivariant prediction with strong performance at the same time.
- By allowing simultaneously and completely modeling interatomic interactions within/across feature spaces in a unified manner, GeoMFormer achieved strong performance covering diverse data modalities, scales and tasks with both invariant and equivariant targets, opening up a new pathway towards scientific AI generalist.
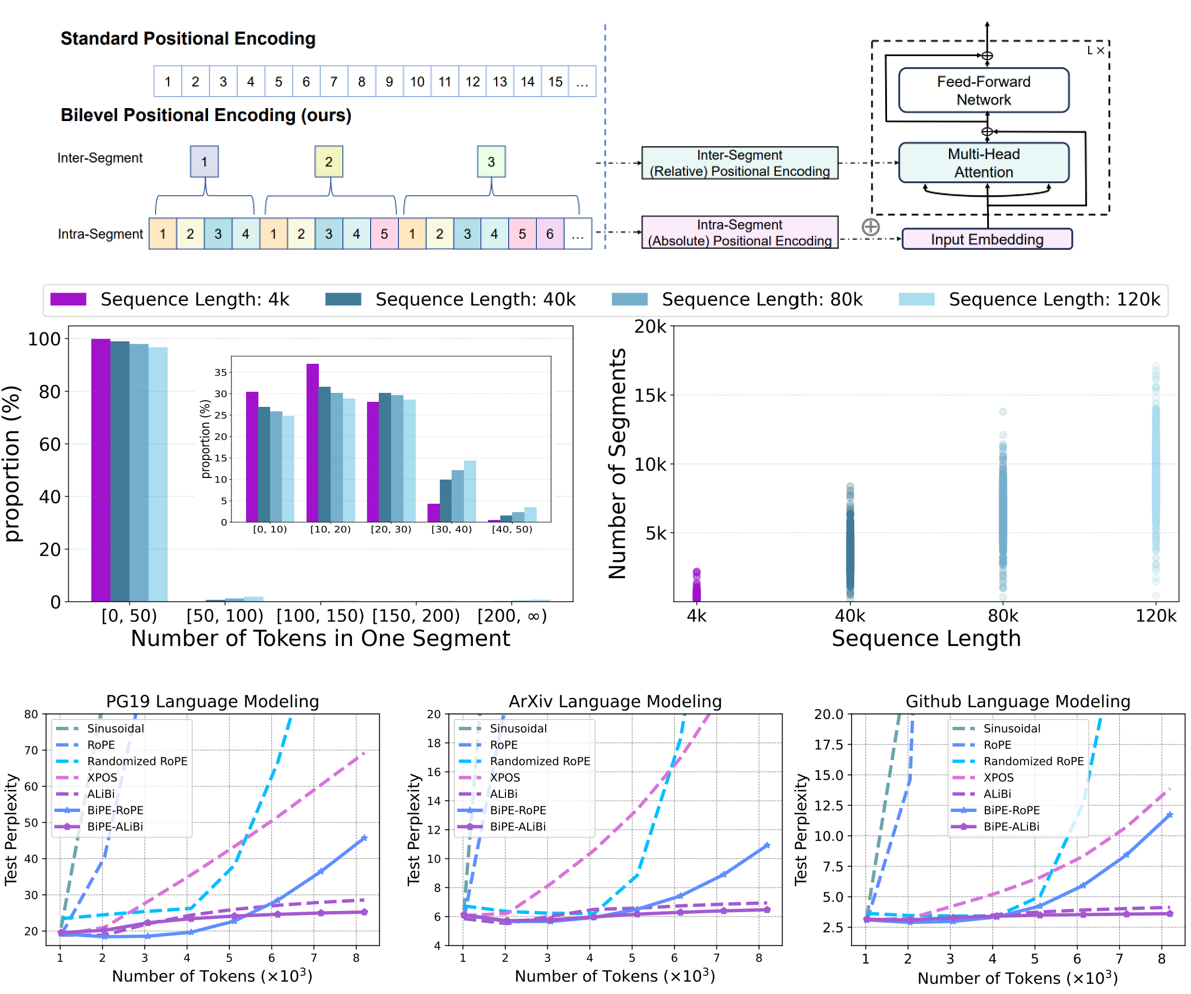
[ICML 2024] Two Stones Hit One Bird: Bilevel Positional Encoding for Better Length Extrapolation
Zhenyu He*, Guhao Feng*, Shengjie Luo*, Kai Yang, Liwei Wang, Jingjing Xu, Zhi Zhang, Hongxia Yang, Di He
- We develop a bilevel positional encoding, which has superior length extrapolation capabilities across diverse text modalities and tasks.
- Leveraging the intrinsic segmentation of language sequences, our BiPE blends an intra-segment encoding and an inter-segment encoding.
- The intra-segment encoding identifies the locations within a segment and helps the model capture the semantic information therein via absolute PE.
- The inter-segment encoding specifies the segment index, models the relationships between segments, and aims to improve extrapolation capabilities via relative PE.
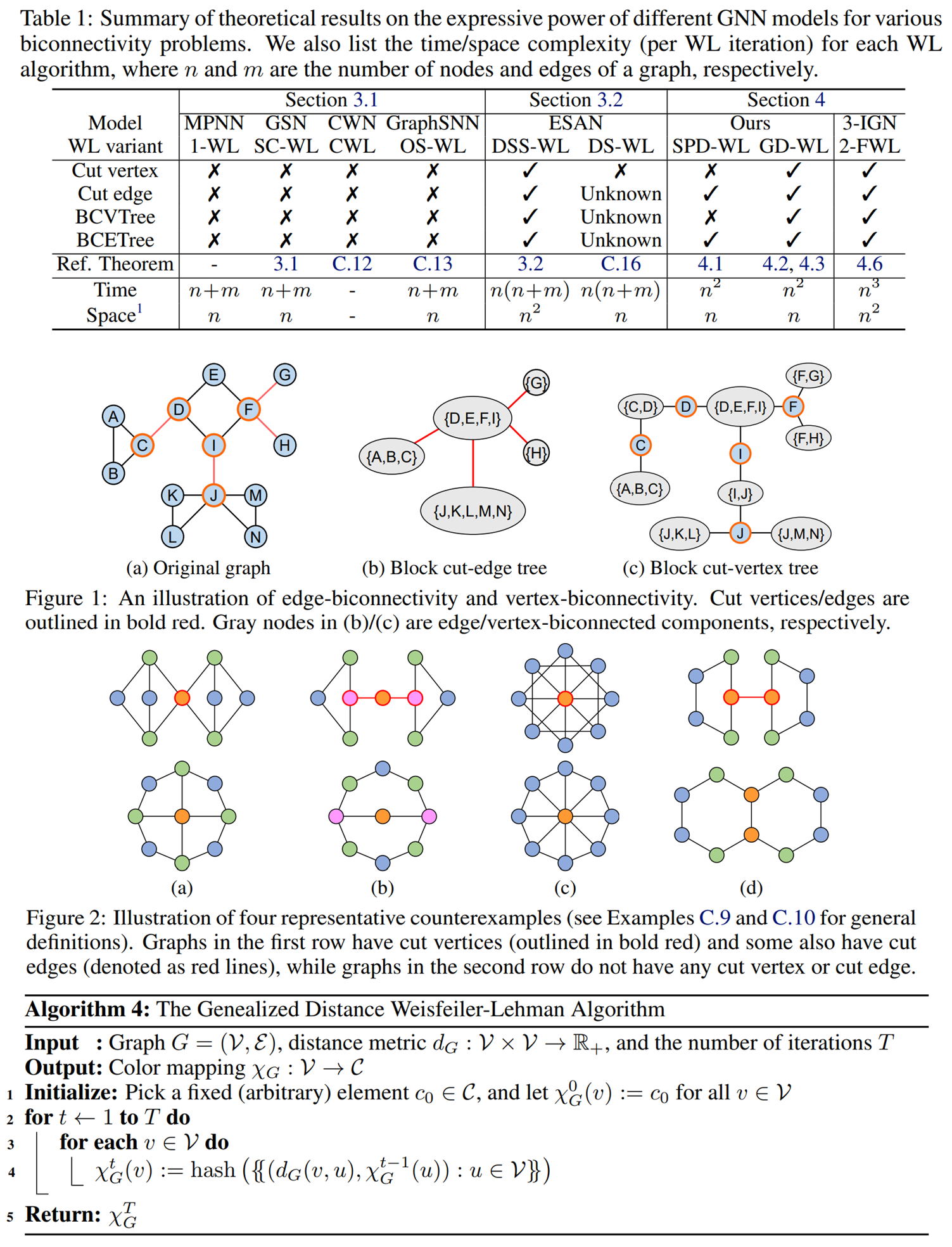
[ICLR 2023 Outstanding Paper Award (top 4/4966)] Rethinking the Expressive Power of GNNs via Graph Biconnectivity
Bohang Zhang*, Shengjie Luo*, Liwei Wang, Di He
- Beyond the WL test, we propose a fundamentally different perspective, a novel class of expressivity metrics via 🚀Graph Biconnectivity🚀, to study the expressive power of GNNs.
- Through the lens of graph biconnectivity, we systematically investigate popular GNNs including classic MPNNs, Graph Substructure Networks (GSN) and its variant, GNN with lifting transformations (MPSN and CWN), GraphSNN, and Subgraph GNNs. The thorough analysis provide a fine-grained understanding on the expressive power of existing GNNs.
- Based on the above theoretical analysis, we develop a principled and more efficient approach, called the Generalized Distance Weisfeiler-Lehman (GD-WL), which is provably expressive for all biconnectivity metrics.
- We further develop Graphormer-GD to implement the GD-WL, which is a Transformer-like architecture that preserves expressiveness and enjoys full parallelizability.
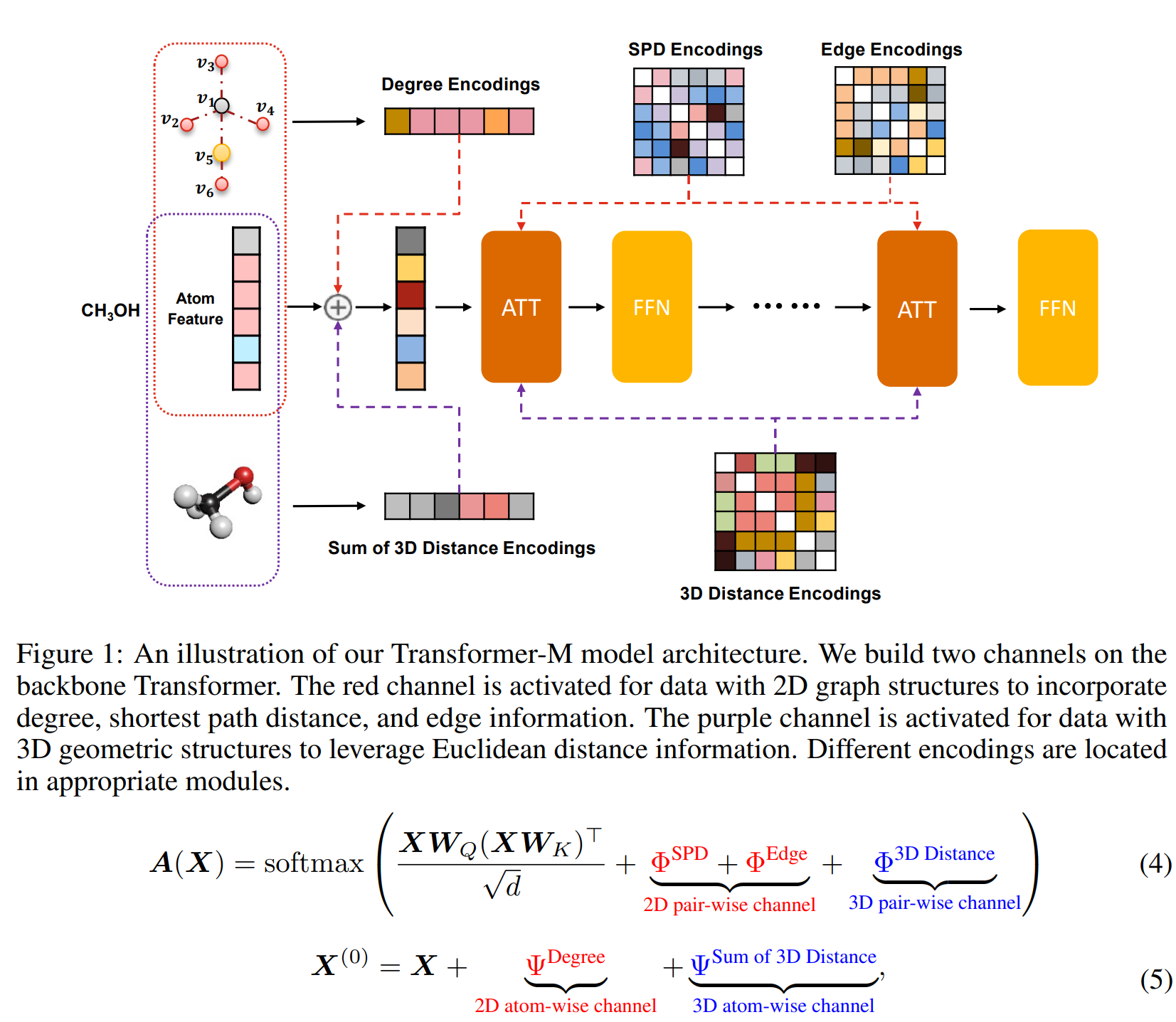
[ICLR 2023] One Transformer Can Understand Both 2D & 3D Molecular Data
Shengjie Luo, Tianlang Chen*, Yixian Xu*, Shuxin Zheng, Tie-Yan Liu, Liwei Wang, Di He
- We develop a novel Transformer-based Molecular model called Transformer-M, which can take molecular data of 2D or 3D formats as input and generate meaningful semantic representations.
- Using the standard Transformer as the backbone architecture, Transformer-M develops two separated channels to encode 2D and 3D structural information and incorporate them with the atom features in the network modules. When the input data is in a particular format, the corresponding channel will be activated, and the other will be disabled.
- We conduct extensive experiments to show that Transformer-M can simultaneously achieve strong performance on 2D and 3D tasks (PCQM4Mv2 (2D), PDBBind (2D+3D), QM9 (3D)), suggesting its broad applicability.
- 🚀 Transformer-M has been used by all Top-3 winners in PCQM4Mv2 Track, 2nd OGB Large-Scale Challenge, NeurIPS 2022!
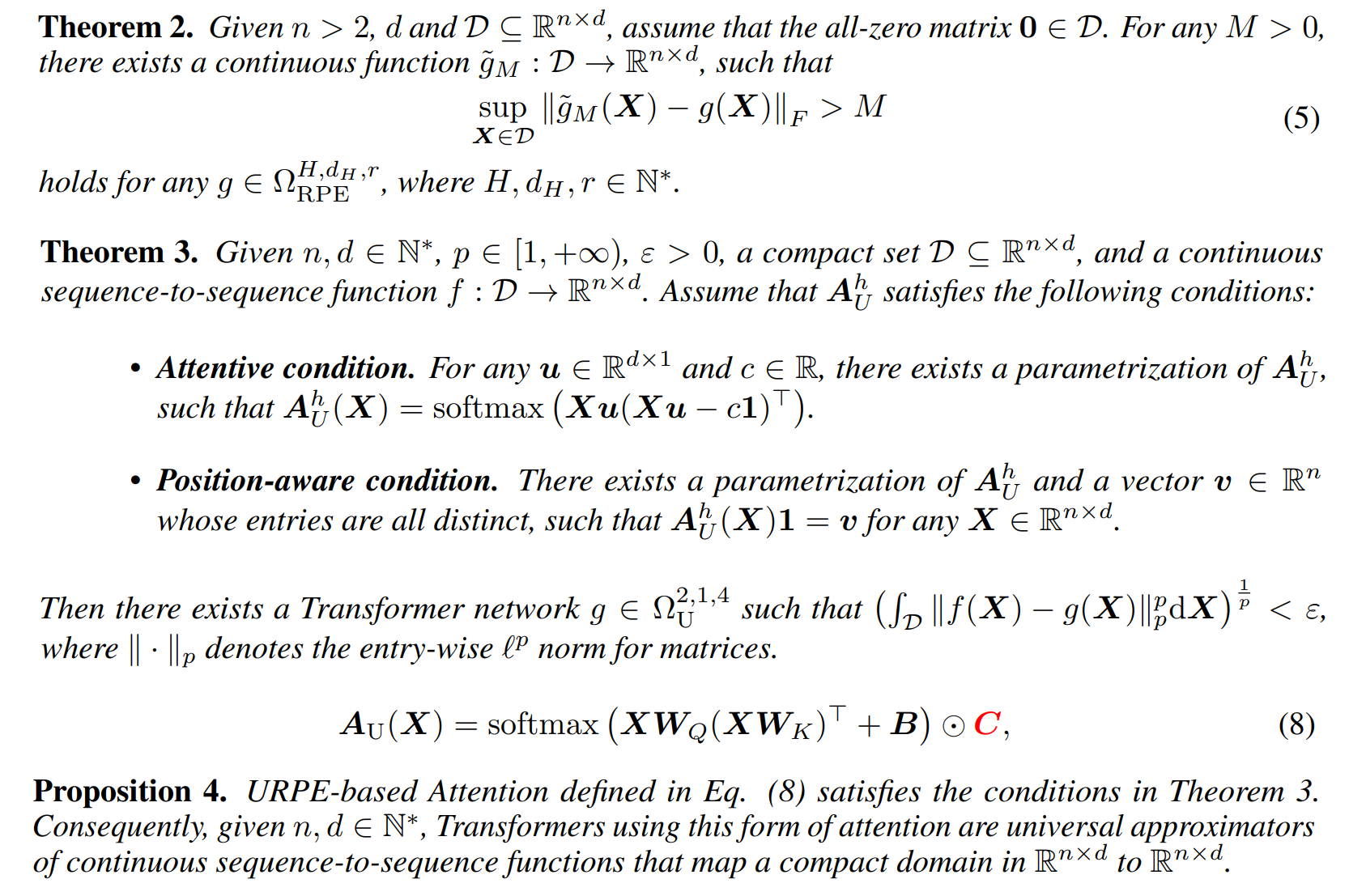
[NeurIPS 2022] Your Transformer May Not be as Powerful as You Expect
Shengjie Luo*, Shanda Li*, Shuxin Zheng, Tie-Yan Liu, Liwei Wang, Di He
- We mathematically analyze the expressive power of RPE-based Transformers, and show that they are not universal approximators of continuous sequence-to-sequence functions.
- We then present sufficient conditions for RPE-based Transformers to achieve universal function approximation. With the theoretical guidance, we develop Universal RPE-based (URPE) Attention, which is easy to implement and parameter-efficient.
- Our URPE-based Transformers are verified to be universal approximators from both theoretical analysis and extensive experiments including synthetic tasks, language modeling and graph learning.
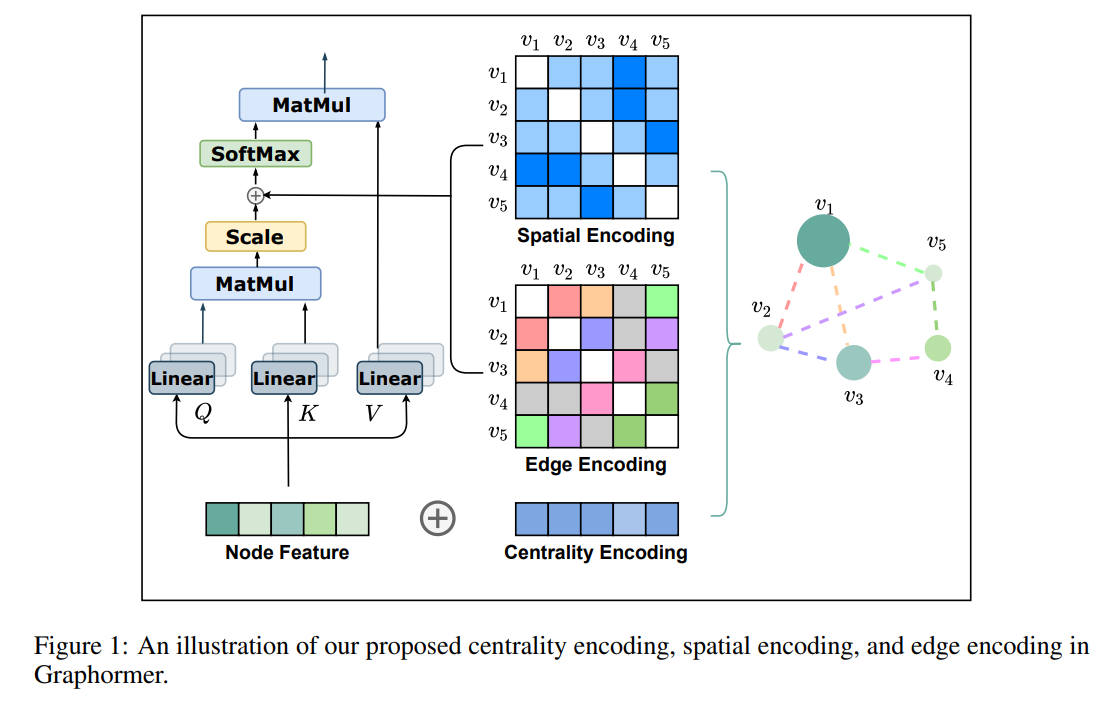
[NeurIPS 2021] Do Transformers Really Perform Badly for Graph Representation?
Chengxuan Ying, Tianle Cai, Shengjie Luo, Shuxin Zheng, Guolin Ke, Di He, Yanming Shen, Tie-Yan Liu
[Project] [Code] [Technical Report] [Slides] [Video]
- Make Transformer great again on graph representation learning by introducing three graph structural encodings.
- Achieve SOTA performance on several benchmarks covering OGB and Benchmarking GNNs.
- 1st place winner of PCQM4M Track, OGB Large-Scale Challenge, KDD CUP 2021.
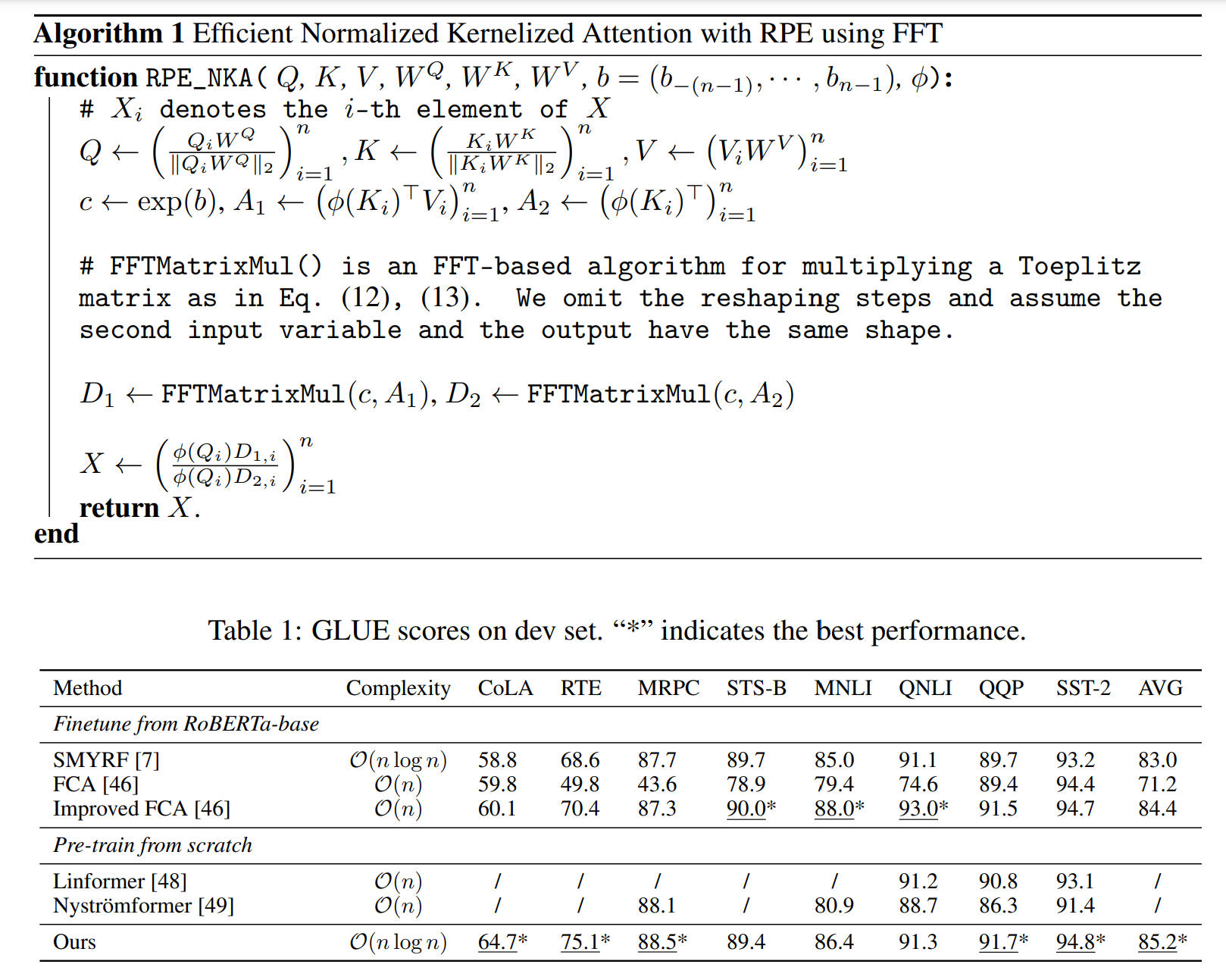
[NeurIPS 2021] Stable, Fast and Accurate: Kernelized Attention with Relative Positional Encoding
Shengjie Luo*, Shanda Li*, Tianle Cai, Dinglan Peng, Di He, Shuxin Zheng, Guolin Ke, Liwei Wang, Tie-Yan Liu
[Project] [Code] [Slides & Video]
- We propose a novel way to accelerate attention calculation (O(nlog(n)) for Transformers with RPE on top of the kernelized attention.
- We mathematically show that kernelized attention with RPE can be calculated efficiently using Fast Fourier Transform (FFT), based on the Toeplitz matrix form of RPE.
- We further demonstrate that properly using RPE can mitigate the training instability problem of vanilla kernelized attention.
- Extensive experiments covering language pre-training, language modeling, Image Classification and Machine Translation are conducted to demonstrate the efficiency and effectiveness of our model.
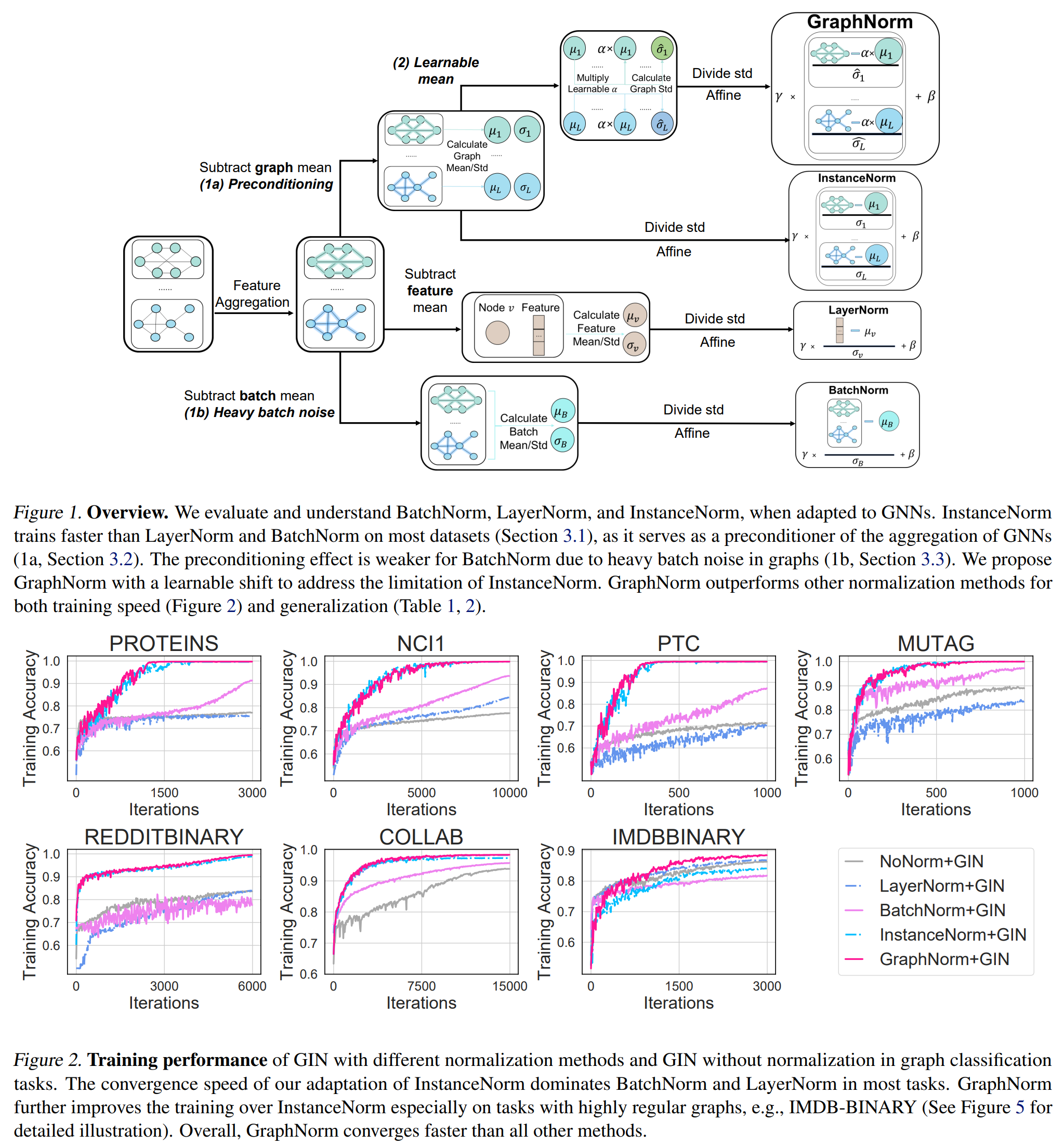
[ICML 2021 Spotlight] GraphNorm: A Principled Approach to Accelerating Graph Neural Network Training
Tianle Cai*, Shengjie Luo*, Keyulu Xu, Di He, Tie-Yan Liu, Liwei Wang
[Code (Official)] [Code (PyG)] [Code (Microsoft ptgnn)]
- We theoretically study the preconditioning effect of normalization methods on GNN training, and empirically observe that the batch noise of graph data is larger than data from other domain, e.g. image data.
- We further show that the shift operation in InstanceNorm can cause expressiveness degradation of GNNs for highly regular graphs.
- Based on these findings, we propose a principled normalization scheme, GraphNorm, and demonstrate its acceleration effect on graph learning benchmarks.
🎖 Honors and Awards
- 2023.03, ICLR 2023 Outstanding Paper Award (top 4/4966) [Link].
- 2021.06, 1st place Winner of PCQM4M Track, OGB Large Scale Challenge, KDD CUP 2021.
- 2018.12, National Scholarship (Top 1%).
📖 Educations
- 2022.09 - 2025.07 (expected), Ph.D. Student, School of Intelligence Science and Technology, Peking University.
- 2020.09 - 2022.07, Master Student, Center for Machine Learning Research, Peking University.
- 2016.09 - 2020.07, Undergraduate Student, Shenyuan Honors College, Beihang University.
💻 Internships
- 2021.12 - now, Machine Learning Group, Microsoft Research Asia, China.
- 2020.10 - 2021.06, Machine Learning Group, Microsoft Research Asia, China.
- 2019.10 - 2020.06, Natural Language Computing Group, Microsoft Research Asia, China.
💬 Invited Talks
- 2025.02, Meta GenAI. Towards Expressive, Efficient, and Scalable Model Design of Neural Networks.
- 2024.06, CCF TCS Outstanding Doctoral Student Forum. Towards Efficient and Effective Geometric Deep Learning.
- 2024.04, AI for Chemistry and Materials Science (AI4CM) Symposium, UC Berkeley \& MIT. Towards Efficient and Effective Geometric Deep Learning for Science.
- 2024.03, FAI Seminar. Enabling Efficient Equivairant Operations in the Fourier Basis via Gaunt Tensor Products.
- 2023.06, FAI Seminar. One Transformer Can Understand Both 2D \& 3D Molecular Data.
- 2023.05, ICLR 2023 Oral Presentation. Rethinking the Expressive Power of GNNs via Graph Biconnectivity.
- 2023.04, Scientific Machine Learning Webinar Series, Carnegie Mellon University. One Transformer Can Understand Both 2D \& 3D Molecular Data.
- 2022.11, Gaoling School of Artificial Intelligence, Renmin University of China. Your Transformer May Not be as Powerful as You Expect.
- 2022.11, AI Time. Your Transformer May Not be as Powerful as You Expect. | [media]
- 2022.03, Huawei Technologies Noah’s Ark Lab. Stable, Fast and Accurate: Kernelized Attention with Relative Positional Encoding.
- 2022.02, AI Time. Stable, Fast and Accurate: Kernelized Attention with Relative Positional Encoding. | [media]
🏫 Professional Services
- Reviewer for ICLR 2022-2025, NeurIPS 2022-2025, ICML 2023-2025, LOG 2022-2024, CVPR 2024-2025, COLM 2024-2025, ICCV 2025.
- Reviewer for Nature Machine Intelligence and Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI).

